TET vs CTET: Differences, Eligibility, Exam Pattern
Table of Contents
Part 1: Understanding TET and CTET - The Essential Teaching Exams
Introduction
You’ve completed B.Ed. Now what? To secure government teaching jobs, you must pass a Teacher Eligibility Test. But which one? TET (conducted by states) or CTET (conducted nationally)?
Most B.Ed graduates ask: “Which exam should I take? Are they equivalent? Can I take both? Which leads to better jobs?”
The confusion is understandable. Both are eligibility tests for government teaching. Both are essential for government jobs. But they’re different exams, different conductors, different validity periods, and different job opportunities. Choosing wrong costs you months of preparation and job opportunities.
This guide clarifies everything: exact differences, eligibility, which to take, preparation strategies, and realistic expectations.
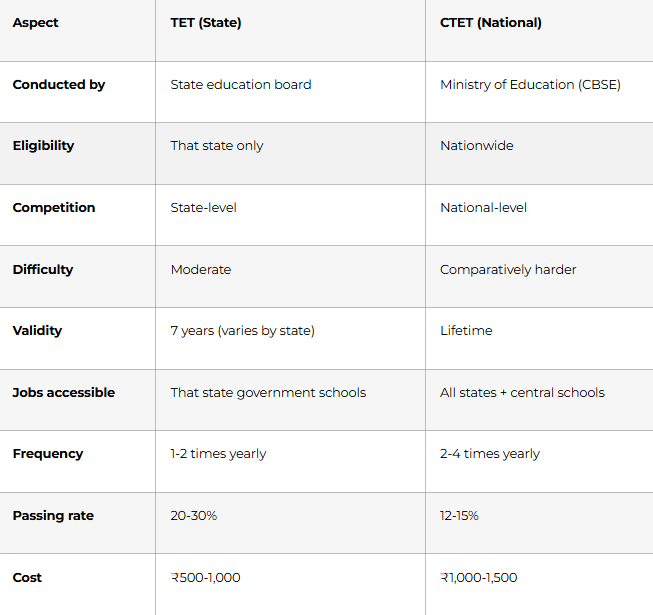
What is TET (Teacher Eligibility Test)?
TET = State-conducted teacher eligibility test
Conducted by: Each state education board (not centrally)
Purpose: Qualify candidates for government teaching jobs in that state
Authority: State SCERT (State Council of Educational Research & Training)
Validity: Typically 7 years (lifetime in some states)
Example:
- Delhi TET conducted by Delhi education board
- Maharashtra TET conducted by Maharashtra education board
- Telangana TET (TS-TET) conducted by Telangana education board
Characteristics:
- ✅ Easier (state-level competition only)
- ✅ Only for that specific state’s jobs
- ❌ Can’t use in another state
- ❌ Different patterns by state
What is CTET (Central Teacher Eligibility Test)?
CTET = National-level teacher eligibility test
Conducted by: Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) on behalf of Ministry of Education
Purpose: Qualify candidates for central government teaching jobs + recognized by most states
Authority: Ministry of Education, Government of India
Validity: Lifetime (permanent once qualified)
Characteristics:
- ✅ Recognized nationwide (all states accept CTET)
- ✅ Prestigious (national standard)
- ✅ Lifetime validity (don’t need to retake)
- ❌ Harder competition (national-level candidates)
- ❌ More rigorous exam
Key Difference Summary
Part 2: Eligibility, Exam Pattern & Structure
TET Eligibility Criteria
Basic eligibility (All states, similar):
✅ Bachelor’s degree (Any discipline)
✅ B.Ed degree (Completed or final year)
✅ Age: No upper age limit (some states have lower limit of 21-25)
✅ Nationality: Indian citizen
✅ No criminal conviction
State-specific variations:
Some states have minor differences:
- Delhi TET: Bachelor’s + B.Ed + Delhi residency (6 months)
- Maharashtra TET: Bachelor’s + B.Ed (no residency requirement)
- Telangana TET: Bachelor’s + B.Ed + Telangana residency (not always strictly enforced)
Example eligibility scenario:
“I’m a B.Sc. graduate with B.Ed from Telangana. Can I take TS-TET?”
Answer: YES! You’re eligible. You can appear and qualify. After qualifying, you can apply for government teaching positions in Telangana schools.
CTET Eligibility Criteria
Bachelor’s degree requirements:
✅ Bachelor’s degree with minimum 50% marks (45% for SC/ST)
✅ B.Ed degree (completed or in final year)
✅ OR D.Ed (Diploma in Education) for primary-only positions
Age limit: None
Nationality: Indian citizen
Example eligibility:
“I have B.A. with 48% marks and B.Ed. Can I take CTET?”
Answer: NO. You need 50% minimum in Bachelor’s. You don’t meet CTET criteria (though you’d be eligible for many state TETs which have lower cutoffs).
TET Exam Pattern & Structure
Pattern varies by state. Example: Telangana TET (TS-TET)
Paper I (Primary level: Classes 1-5):
- Duration: 2.5 hours
- Questions: 150 MCQ
- Sections:
- Child Development & Pedagogy: 30 Q
- Language I (English/Regional): 30 Q
- Language II (Hindi/English/Regional): 30 Q
- Mathematics: 30 Q
- Environmental Studies: 30 Q
- Total marks: 150
- Passing: 90+ marks (typically 60%)
Paper II (Secondary level: Classes 6-10):
- Duration: 2.5 hours
- Questions: 150 MCQ
- Sections:
- Child Development & Pedagogy: 30 Q
- Language I: 30 Q
- Language II: 30 Q
- Subject specialization (Math/Science/Social Studies/English): 60 Q
- Total marks: 150
- Passing: 90+ marks (typically 60%)
Other states’ patterns (broadly similar):
- Most states: 2 papers, ~150 questions, 2.5 hours each
- Sections similar: Child development, languages, subject knowledge
- Passing marks: Usually 60-65% (varies by state)
CTET Exam Pattern & Structure
Paper I (Primary: Classes 1-5):
- Duration: 2.5 hours
- Questions: 150 MCQ
- Sections:
- Child Development & Pedagogy: 30 Q
- English: 30 Q
- Hindi: 30 Q
- Mathematics: 30 Q
- Environmental Studies: 30 Q
- Total marks: 150
- Passing: 90+ marks (60% typically)
Paper II (Secondary: Classes 6-8):
- Duration: 3 hours
- Questions: 150 MCQ
- Sections:
- Child Development & Pedagogy: 30 Q
- English: 30 Q
- Hindi: 30 Q
- Mathematics (if Math teacher): 30 Q
- OR Science (if Science teacher): 30 Q
- OR Social Studies (if Social Studies teacher): 30 Q
- Total marks: 150
- Passing: 90+ marks (60%)
Paper II (Secondary: Classes 6-12):
- Duration: 3.5 hours
- Similar structure but more in-depth
Key differences from TET:
- More rigorous subject-specific questions
- Harder pedagogy questions
- National-level benchmark (stricter)
- Uniform across country (no state variations)
Part 3: Which Exam to Take - Decision Framework
Take TET If...
✅ You want to teach in specific state
- Not interested in moving to other states
- Want to settle in home state
- Example: Maharashtra graduate wanting to teach in Maharashtra only
✅ You want easier exam
- TET passes more candidates (20-30% vs CTET 12-15%)
- Less competition
- Slightly easier questions
- Prefer lower-stakes exam
✅ You need quick qualification
- TET conducted more frequently (sometimes 3-4 times yearly)
- Can appear sooner
- Get qualified faster
✅ You have limited preparation time
- TET requires less intense preparation
- CTET needs deeper subject knowledge
✅ You’re not confident in English/Hindi
- Many TETs have flexibility on languages
- Some TETs allow regional languages more
- CTET strictly English/Hindi
Take CTET If...
✅ You want maximum job opportunities
- Can teach in any state (CTET recognized everywhere)
- Not limited to one state
- More government posts accessible
✅ You want lifetime validity
- CTET valid for life (no retakes needed)
- TET valid 7 years (need to requalify)
- If you want security for decades, CTET is better
✅ You aspire to leadership roles
- CTET preferred for promotions and leadership
- Better credential for higher positions
- International schools respect CTET more
✅ You’re academically strong
- Willing to work harder
- Confident in competitive exam
- Want prestige of national qualification
✅ You might relocate later
- Not sure where you’ll teach in future
- CTET keeps options open
- TET locks you to one state
✅ You want to teach in central government schools
- Kendriya Vidyalayas (KV)
- Navodaya Vidyalayas (NV)
- Central schools often prefer/require CTET
- TET doesn’t qualify for these
Decision Matrix: Which Exam is Right for You?

Part 4: Eligibility for Different Government Jobs
Jobs with TET Qualification
After passing state TET, you’re eligible for:
✅ Government school teaching (that state only)
- Primary schools (Classes 1-5) with Paper I
- Secondary schools (Classes 6-10) with Paper II
- Senior secondary (Classes 11-12) with Paper II (if eligible)
✅ State-specific government positions
- Example: After passing Telangana TET, eligible for TS government schools only
❌ NOT eligible for:
- Kendriya Vidyalaya (requires CTET)
- Navodaya Vidyalaya (requires CTET)
- Any other state’s government schools
- Central government schools
Jobs with CTET Qualification
After passing CTET, you’re eligible for:
✅ All state government schools (any state)
- Pass CTET once → Can teach in any state’s government schools
- Huge advantage: Portable across country
✅ Central government schools:
- Kendriya Vidyalayas (KV) – central government schools
- Navodaya Vidyalayas (NV) – residential schools
- Delhi Cantonment Board schools
- Other central-funded institutions
✅ Priority in government recruitment
- CTET holders often get priority in merit lists
- Some states give additional marks for CTET
❌ What CTET doesn’t do:
- Doesn’t guarantee job (still must apply, interview)
- Doesn’t give preferential treatment over TET in state-specific hiring
- For state-specific positions, TET and CTET equally valid
Realistic Job Outcomes
TET qualified candidate (Telangana, for example):
✅ Can apply for: TS government primary/secondary schools
❌ Cannot apply for: Any other state, Kendriya Vidyalaya, central schools
🎯 Job prospects: Good in that state, zero outside
CTET qualified candidate:
✅ Can apply for: All states + central schools
❌ Cannot apply for: Only those with specific state eligibility (rare)
🎯 Job prospects: Excellent across country, very mobile
Part 5: Passing Rates, Difficulty & Success Strategies
Passing Rates & Statistics

Key insight: CTET is objectively harder (passing rate 12-15% vs TET 20-30%).
Why CTET is harder:
- National-level competition (stronger candidates)
- Stricter evaluation standards
- More rigorous subject-specific questions
- Higher baseline expectations
Difficulty Comparison: Topic-wise

Preparation Strategy: TET
Timeline: 4-6 months sufficient
Study plan:
- Month 1-2: Child development + pedagogy (40% of content)
- Month 2-3: Language 1 (English)
- Month 3-4: Language 2 (Hindi/Regional)
- Month 4-5: Subject knowledge (Math/Science/Social Studies/EVS)
- Month 5-6: Revision + mock tests
Daily schedule:
- 2-3 hours study daily
- 1 hour mock tests weekly
- 1 hour current affairs (if included)
Resources:
- Books: Standard TET preparation books (₹200-500 each)
- Online: YouTube channels, paid courses (₹1,000-3,000)
- Mock tests: 20-30 full-length tests
- Groups: Join TET preparation groups for peer learning
Success tips:
- Know state-specific TET pattern (varies by state)
- Practice previous year papers (important!)
- Focus on scoring 60%+ (doesn’t need 90%+)
- Memorize important definitions, dates, concepts
Preparation Strategy: CTET
Timeline: 6-9 months recommended
Study plan:
- Month 1-2: Deep dive child development (interconnected with psychology)
- Month 2-3: Pedagogy (critical for CTET – very detailed)
- Month 3-4: Language 1 (English – rigorous grammar focus)
- Month 4-5: Language 2 (Hindi – literature + grammar)
- Month 5-6: Subject specialization (very deep knowledge required)
- Month 6-9: Revision + continuous mock tests
Daily schedule:
- 3-4 hours study daily (more than TET)
- 2 hours mock tests weekly (more rigorous)
- 1 hour subject revision daily
Resources:
- Books: CTET-specific books (₹300-600 each)
- Online: CTET coaching (₹5,000-10,000 for comprehensive course)
- Mock tests: 50+ full-length tests (at least double TET)
- Reference material: NCERT books (especially for social studies, science)
Success tips:
- CTET tests deeper understanding, not just memorization
- Practice subject-specific questions (30-40% of paper)
- Take regular mock tests to assess progress
- Join CTET study groups online
- Subscribe to CTET update channels for pattern changes
- Need 60%+ to pass, but aim for 70-75% (gives cushion)
Part 6: Can You Take Both TET and CTET?
Yes, You Can Take Both
Good news: There’s no rule against taking both TET and CTET. Many candidates do.
Benefits of taking both:
✅ Maximum options: If qualified for both, can apply anywhere
✅ Backup plan: If fail one, other is backup
✅ Lifetime security: CTET lifetime + TET 7 years = combined security
✅ More job opportunities: Access to both state and central schools
Realistic timeline:
- Prepare for both simultaneously: 8-10 months
- OR Prepare for TET first, then CTET: 10-12 months total
- OR Prepare for CTET first, then TET: 8-10 months total (CTET preparation covers TET requirements)
Recommended Approach: CTET First, Then TET
- CTET preparation covers TET: If you study for rigorous CTET, TET will be easier. Reverse isn’t true—TET prep doesn’t fully prepare for CTET.
- Efficiency: Study once for harder exam, then practice easier exam.
- Lifetime security: CTET provides lifetime validity; TET provides backup.
Timeline:
- Month 1-8: Intensive CTET preparation
- Month 6-8: Take CTET (attempt after 5-6 months prep)
- Month 7-9: Light TET-specific preparation
- Month 9: Take TET (easier now after CTET prep)
- Result: Both qualifications within 9 months
Real scenario:
“I prepared 6 months for CTET and took exam in July. Didn’t pass (score 62%, needed 63%). Then took TET in September with just 2 weeks prep, and passed easily. Now I’m taking CTET again in December.”
Who Should Take Both?
✅ Take both if:
- You’re serious about government teaching
- You want maximum job options
- You can afford time/resources
- You’re academically capable
❌ Take only TET if:
- You’re sure you want to teach only in one state
- You have limited time/resources
- You want quicker path to job
- You prefer less competition
❌ Take only CTET if:
- You might relocate
- You want lifetime validity
- You prefer prestige of national exam
- You’re very strong academically
Part 7: Validity, Retakes & Long-term Strategy
Validity Periods

Example scenarios:
Scenario 1: TET only
- Pass TET in 2025, valid until 2032
- After 2032: Must retake TET to apply
- Implication: Ongoing requalification required
Scenario 2: CTET only
- Pass CTET in 2025, valid forever
- After 2032: Still valid, no retake needed
- Implication: One-time qualification
Scenario 3: Both TET + CTET
- Pass both in 2025
- TET valid until 2032, CTET forever
- Implication: If CTET passed, you’re set for life
Re-attempting Failed Exam
If you fail TET:
- Can retake immediately (usually next cycle, 3-6 months later)
- Unlimited attempts allowed
- Each attempt is separate
If you fail CTET:
- Can retake immediately (conducted 2-4 times yearly)
- No limit on attempts
- BUT lifetime validity once passed (so worth investing in)
Strategy: Most candidates pass within 2-3 attempts.
Long-term Career Impact
TET + Government job pathway (30-year career):
text
2025: Pass TET
2026-2032: Work as government teacher (secure job, ₹5-6L/year)
2032: TET expires, must retake to continue government job
2033-2039: Continue teaching (after retaking TET)
2039: Retirement or further career shift
CTET + Government job pathway (30-year career):
text
2025: Pass CTET
2026-2055: Secure government teaching (any state, job secure)
No requalification needed ever
Lifetime security
Insight: CTET provides genuine lifetime security; TET requires periodic requalification.
Part 8: Making Your Final Decision - Action Plan
Decision Checklist
Answer these honestly:
- Will you stay in one state only?
- YES → TET sufficient (take TET)
- NO → CTET better (take CTET)
- How strong are you academically?
- Average → TET easier (choose TET)
- Strong → CTET achievable (choose CTET)
- How much time can you invest?
- 4-5 months → TET (quicker)
- 8-10 months → CTET (longer needed)
- Do you want lifetime security?
- YES → CTET (lifetime validity)
- NO → TET (7 years enough)
- Do you want maximum job options?
- YES → CTET (all states + central schools)
- NO → TET (one state okay)
- Your ideal career 5 years from now?
- “Settled in home state teaching” → TET
- “Teaching anywhere in India” → CTET
- “Exploring options” → CTET first (safer bet)
Recommended Pathways
Pathway 1: TET-only (Fastest)
- Timeline: 6 months to job
- Effort: 4-5 months study
- Cost: ₹5,000-10,000
- Best for: State-specific, moderate students, quick job need
Pathway 2: CTET-only (Safest)
- Timeline: 9-12 months to job
- Effort: 7-9 months study
- Cost: ₹10,000-15,000
- Best for: Ambitious, mobile, want lifetime security
Pathway 3: CTET + TET (Comprehensive – Recommended)
- Timeline: 9-12 months, both qualified
- Effort: 8-10 months (combined)
- Cost: ₹15,000-25,000
- Best for: Want all options, serious about teaching, resources available
Month-by-Month Action Plan
Month 1: Decision & Planning
✅ Decide which exam(s) to take
✅ Research state-specific TET pattern (if taking TET)
✅ Gather study materials
✅ Join preparation groups
Month 2-3: Foundation
✅ Study child development thoroughly
✅ Learn pedagogy concepts
✅ Understand exam pattern deeply
Month 4-5: Content Mastery
✅ Complete languages section
✅ Study subject knowledge
✅ Take first mock test
Month 6-7: Intensive Preparation
✅ Daily mock tests
✅ Revision of weak areas
✅ Speed building for exam day
Month 8-9: Final Push
✅ Attempt exam (TET and/or CTET)
✅ Await results
✅ If passed: Start job search and applications
Complete Comparison Table
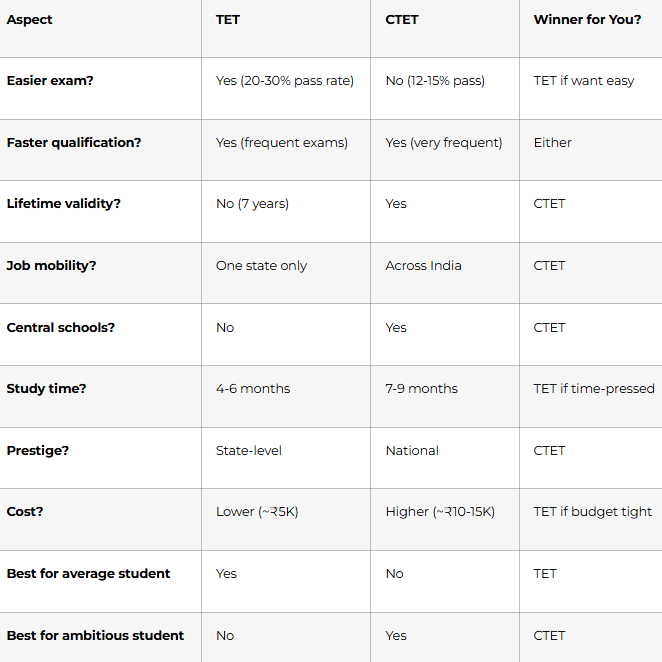
Complete Comparison Table
If I had to recommend one path for most B.Ed graduates:
→ Take CTET first, then TET
Why?
- Maximizes options: Once CTET qualified, you have national access
- CTET preparation is harder: Learning this prepares you for TET automatically
- Lifetime security: CTET never expires
- Central school access: Opens Kendriya Vidyalaya + NV positions (premium jobs)
- Insurance: TET becomes backup (if CTET delayed, TET still gets you state job)
- Career flexibility: Not locked into one state
But if you’re time-pressed or state-specific, TET alone is perfectly valid.
