Quick Reference Resources
Table of Contents
Blog Content:
Introduction: Your Last-Minute Companion
Module 7 is your quick-access companion during final revision. Rather than re-reading lengthy explanations, you’ll find organized formula banks, memory tricks, calculation shortcuts, and red flags that indicate common mistakes. Print this module or bookmark it—you’ll return to it repeatedly in the days before your exam.
📘 Explore Full Learning Resources — Access structured courses, practice modules, and exams to strengthen your Quant & Reasoning fundamentals.
Section 1: Formula Cheat Sheet - Organized by Topic
QUANTITATIVE APTITUDE FORMULAS
Number Systems & Simplifications
Percentages & Ratios

Profit & Loss

Interest Calculations

Speed, Distance, Time
Work & Time

Progressions

Set Theory

Probability

📝 Continue Your Learning Journey — Discover more improvement guides, skill-building posts, and preparation tips.
Section 2: Tips and Tricks Compilation
CALCULATION SHORTCUTS
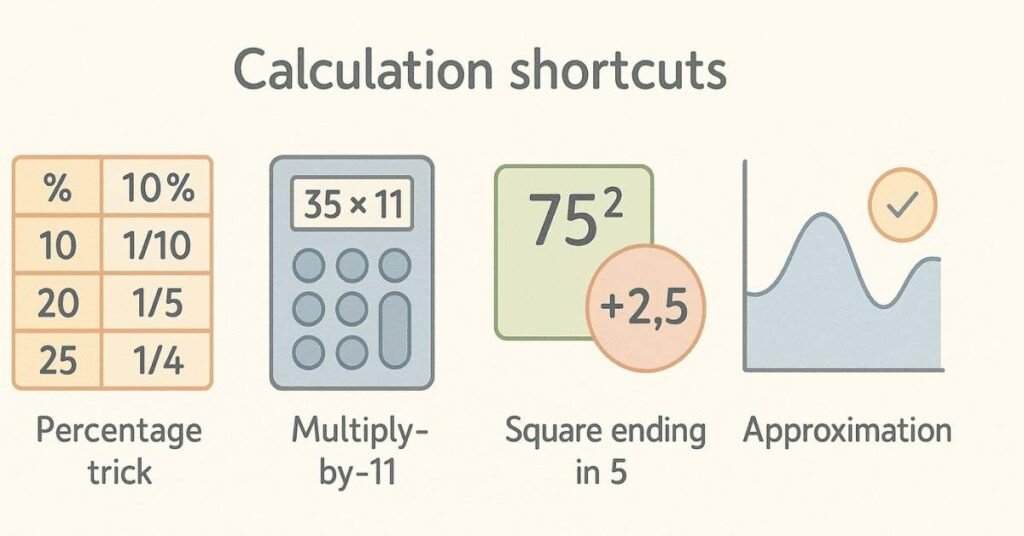
Trick 1: Percentage Shortcut (5-10-20-25 Rule)
Instead of: 20% of 350 = 0.20 × 350 = 70
Think: 20% = 1/5, so 350÷5 = 70 (Much faster!)
Trick 2: Multiply by 11 Instantly
To multiply any 2-digit number by 11:
- 23 × 11: Place digits apart (2_3), add them (2+3=5), put in middle → 253
- 47 × 11: 4_7 → 4+7=11, carry over → 517
Trick 3: Squaring Numbers Ending in 5
To square numbers ending in 5:
- 25² = (2×3)|25 = 6|25 = 625
- 35² = (3×4)|25 = 12|25 = 1225
- 45² = (4×5)|25 = 20|25 = 2025
Formula: (n5)² = [n(n+1)]|25
Trick 4: Speed-Distance-Time Conversion
Instead of remembering km/h to m/s conversion formula:
km/h to m/s: Multiply by 5/18
m/s to km/h: Multiply by 18/5
Easy way: 72 km/h = 72 × 5/18 = 20 m/s
Quick: 72 ÷ 3.6 = 20 (since 18/5 = 3.6)
Trick 5: Percentage Increase Formula Shortcut
If price increased by 25%, new price = 125% of old
Instead of: (125/100) × old price
Think: 1.25 × old price (one multiplication instead of two)
LOGICAL REASONING SHORTCUTS
Trick 1: Venn Diagram for Syllogisms
Always draw three overlapping circles for:
- Major term
- Minor term
- Middle term
If you can’t draw a valid diagram, conclusion is invalid.
Trick 2: Blood Relations Quick Map
text
Parent’s sibling = Aunt/Uncle
Sibling’s child = Nephew/Niece
Aunt/Uncle’s child = Cousin
Sibling’s spouse = Brother/Sister-in-law
Rule: If you get confused, trace one person at a time.
Trick 3: Coding-Decoding Pattern Recognition
Before attempting: Check if it’s
- Letter shift (A→B, B→C)?
- Position-based? (1st letter +2, 2nd letter +3)?
- Alternating? (vowels stay, consonants shift)?
- Reverse? (word written backward)?
Identifying pattern first saves 60% of calculation time.
Trick 4: Series Pattern Hierarchy
Check patterns in this order:
- Arithmetic (constant difference)?
- Geometric (constant ratio)?
- Fibonacci (sum of previous two)?
- Square/Cube (perfect powers)?
- Position-based (alternate between patterns)?
Most series fit one of these five. Test them methodically instead of guessing.
Section 3: Common Pitfall Indicators
RED FLAGS THAT SIGNAL MISTAKES
Pitfall 1: “Per” vs “Total” Confusion
Red Flag: Question uses “per” but you calculated total (or vice versa)
Example: “Average salary per employee is ₹50,000. Company has 100 employees. What’s total salary?”
- Wrong: Answer = 50,000 (forgot to multiply by 100)
- Right: Answer = 50,000 × 100 = ₹50 lakhs
Prevention: Circle the word “per” or “total” before calculating.
Pitfall 2: Wrong Base Division
Red Flag: Profit % calculated as (Profit/Selling Price) instead of (Profit/Cost Price)
Example: CP = ₹100, SP = ₹150
- Wrong: Profit% = 50/150 × 100 = 33.33%
- Right: Profit% = 50/100 × 100 = 50%
Prevention: Remember: Percentage always divides by the original/starting value.
Pitfall 3: Forgetting Unit Conversion
Red Flag: Calculating with mixed units (₹ crores and ₹ lakhs in same problem)
Prevention: Convert all to same unit before any calculation.
Pitfall 4: Average Speed Error
Red Flag: Adding speeds and dividing by 2 instead of using distance/time
Example: 60 km/h for 200 km, then 40 km/h for 200 km
- Wrong: Average = (60+40)/2 = 50 km/h
- Right: Total distance = 400, Total time = 200/60 + 200/40 = 3.33 + 5 = 8.33 hours; Avg = 400/8.33 = 48 km/h
Prevention: Average speed = TOTAL DISTANCE ÷ TOTAL TIME (always)
Pitfall 5: “Some” Interpreted as “All”
Red Flag: Concluding “All A are C” from “All A are B” and “Some B are C”
Prevention: “Some” means at least one, not all. “Some” cannot lead to “All” conclusions.
Pitfall 6: Percentage Point vs Percentage Confusion
Red Flag: “Sales increased from 20% to 25%”
Is this:
- 25% (5 percentage points increase)?
- Or 125% of original (25% is 125% of 20%, so 5% increase)?
Prevention: Read carefully. If comparing percentages: 25%-20% = 5 percentage points. If calculating increase: (25-20)/20 × 100 = 25% increase.
Pitfall 7: Compound Interest vs Simple Interest
Red Flag: Using SI formula when CI is required (or vice versa)
Prevention: Check: “interest on interest” or “accumulated” → use CI. Otherwise → use SI.
Pitfall 8: Intersection vs Union Confusion
Red Flag: Calculating people who used BOTH services when question asks people who used AT LEAST ONE
Prevention: Read: “both” = intersection (∩); “either/or/at least one” = union (∪)
Pitfall 9: Time Miscalculation
Red Flag: Calculating work done after time T, but forgetting to multiply work rate by T
Example: A’s rate = 1/10 per day. After 3 days, work done = ?
- Wrong: Answer = 1/10 (forgot to multiply by 3)
- Right: Answer = 1/10 × 3 = 3/10
Prevention: Always: Work Done = Rate × Time
Pitfall 10: Ratio Simplification Error
Red Flag: Adding numerator and denominator separately instead of using common ratio
Example: If A:B = 2:3 and A = 100
- Wrong: A:B = 2:3 means A=2, B=3 (but actual A=100, so B=150? No, this is wrong reasoning)
- Right: A = 2x = 100, so x = 50, then B = 3x = 150
Prevention: Always use variable (x or k) when working with ratios; don’t use raw ratio values.

Section 4: Success Benchmarks and Performance Metrics
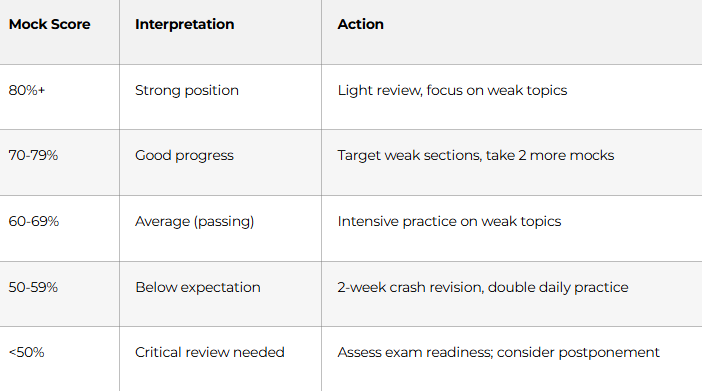
SCORE INTERPRETATION GUIDE
What Your Mock Test Score Means:
Company-Specific Score Benchmarks:

Section-Wise Performance Goals
Quantitative Aptitude:
- Beginner: 50-60% accuracy
- Intermediate: 65-75% accuracy
- Advanced: 80%+ accuracy
- Time goal: 1.5-2 minutes per question
Logical Reasoning:
- Beginner: 55-65% accuracy
- Intermediate: 70-80% accuracy
- Advanced: 85%+ accuracy
- Time goal: 1-1.5 minutes per question
Verbal Ability:
- Beginner: 60-70% accuracy
- Intermediate: 75-85% accuracy
- Advanced: 90%+ accuracy
- Time goal: 1 minute per question
What Score Improvement Means

📊 Upgrade Your Preparation Strategy — Get step-by-step frameworks, study plans, and shortcuts to boost accuracy and speed
Section 5: Last-Minute Revision Checklist (24 Hours Before Exam)
Morning of Exam Day (Do This, Nothing Else)
- Review time allocation strategy (5 min)
- Glance at formula summary (not re-learning, just refreshing) (10 min)
- Practice 2-3 easy problems to build confidence (10 min)
- Light breakfast, stay hydrated
- Arrive 30 min early
Do NOT Do:
- ❌ Learn new concepts (will confuse you)
- ❌ Solve difficult problems (will demoralize)
- ❌ Discuss exam with others (will create doubt)
- ❌ Check solutions to yesterday’s practice (will stress you)
Section 6: One-Page Quick Reference (Print & Keep Handy)
FORMULA SUMMARY – ONE PAGE
text
QUICK FORMULAS FOR REVISION
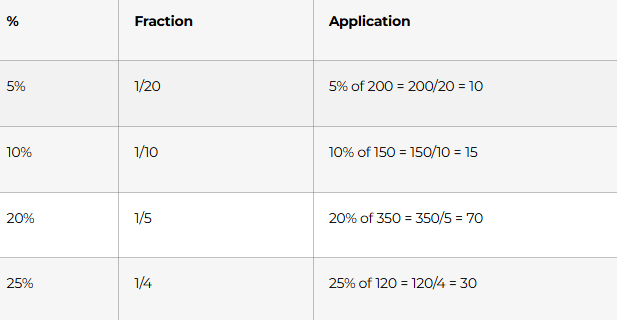
PERCENTAGES: 5%=1/20, 10%=1/10, 20%=1/5, 25%=1/4
P&L: Profit% = (SP-CP)/CP × 100 [Divide by CP, not SP]
INTEREST: A = P(1+R/100)^T [For compound interest]
AVERAGES: Total ÷ Count [For average speed: Total Distance ÷ Total Time]
RATIOS: Use variable x; A = ax, B = bx (where a:b is ratio)
AP: Tn = a + (n-1)d | Sn = n/2[2a + (n-1)d]
PERMUTATION: nPr = n!/(n-r)! | COMBINATION: nCr = n!/(r!(n-r)!))
SETS: n(A∪B) = n(A) + n(B) – n(A∩B)
PROBABILITY: P(E) = Favorable/Total | P(A AND B) = P(A) × P(B)
WORK: Rate = 1/Time | Combined Rate = 1/T_A + 1/T_B
