BRAND MANAGER CAREER GUIDE
Table of Contents
What is a Brand Manager and Why is This Role Critical?
Brand managers are the guardians and architects of a company’s brand identity. When you think of Nike and instantly feel inspired, or Amul and smile at their clever advertisements, or Patanjali and associate it with natural products—that’s the work of brand managers shaping perception, building emotional connections, and positioning brands in consumers’ minds.
Unlike other marketing roles focused on specific channels (social media, SEO, paid ads), brand managers take a holistic view. They shape the entire brand experience—from logo and visual identity to messaging tone, product positioning, customer experience, and long-term brand equity. They’re strategic thinkers who ask: “What should our brand stand for? How do we differentiate from competitors? How do we connect emotionally with our target audience?”
In India’s competitive market with thousands of brands vying for attention across categories, skilled brand managers command premium salaries and influence major business decisions. They don’t just market products—they build brands that become part of customers’ lives and identities.
What Brand Managers Actually Do Daily
Brand management combines strategic planning with tactical execution
Strategic Planning
- Develop comprehensive brand strategies aligned with business objectives
- Define brand positioning—what makes the brand unique and relevant
- Create brand guidelines ensuring consistency across all touchpoints
- Conduct market research to understand consumer needs, preferences, and perceptions
- Analyze competitive landscape and identify differentiation opportunities
- Set annual brand goals and KPIs (awareness, consideration, preference, loyalty)
Campaign Management
- Plan and execute multi-channel marketing campaigns across digital and traditional media
- Collaborate with creative agencies on advertising development
- Oversee campaign production from concept to launch
- Manage campaign budgets ensuring efficient allocation
- Monitor campaign performance and adjust strategies based on results
Cross-Functional Collaboration
- Work with product teams on new product development and launches
- Coordinate with sales teams to align brand messaging with sales goals
- Partner with design teams to maintain visual brand consistency
- Collaborate with customer service to ensure brand promises are kept
- Present brand strategies and results to senior management
Market Research and Analysis
- Conduct consumer research through surveys, focus groups, and interviews
- Analyze market trends and consumer behavior shifts
- Track brand health metrics—awareness, consideration, Net Promoter Score
- Monitor competitor activities and industry developments
- Use insights to refine brand strategy and messaging
Budget and Resource Management
- Manage brand marketing budgets (often in crores for large brands)
- Allocate resources across campaigns and channels
- Evaluate ROI of marketing investments
- Make trade-offs between short-term sales and long-term brand building
Essential Skills for Brand Managers
Strategic Thinking
Brand Strategy Development: Ability to define brand positioning, target audience, value proposition, and personality that differentiate from competitors.
Long-Term Vision: Thinking beyond quarterly sales to build sustainable brand equity over years while balancing short-term business pressures.
Market Understanding: Deep insight into consumer psychology, cultural trends, competitive dynamics, and industry evolution.
Analytical Skills
Data Interpretation: Analyzing market research, campaign performance, sales data, and brand health metrics to make informed decisions.
ROI Measurement: Quantifying brand marketing’s business impact—though brand building effects often take time to materialize.
Consumer Insight Development: Translating raw data into meaningful insights about consumer needs, motivations, and behaviors.
Creative and Communication Skills
Storytelling: Crafting compelling brand narratives that resonate emotionally with target audiences.
Creative Briefing: Clearly articulating brand strategy to creative agencies and internal teams so they produce work aligned with brand vision.
Presentation Skills: Presenting brand strategies, campaign proposals, and results to senior management and stakeholders persuasively.
Brand Voice Development: Defining how the brand should communicate—formal vs. casual, humorous vs. serious, premium vs. accessible.
Leadership and Collaboration
Cross-Functional Leadership: Influencing teams you don’t directly manage (sales, product, design) to align with brand strategy.
Stakeholder Management: Managing expectations and building consensus among diverse internal and external stakeholders.
Agency Management: Briefing and managing relationships with creative agencies, media agencies, and other external partners.
Project Management: Coordinating complex campaigns involving multiple teams, vendors, and workstreams with tight deadlines.
India-Specific Skills
Cultural Sensitivity: Understanding regional differences in preferences, language, traditions, and consumer behavior across India’s diverse market.
Regional Marketing: Adapting brand strategies for different states and cities while maintaining overall brand consistency.
Festival Marketing: Leveraging India’s numerous festivals (Diwali, Durga Puja, Onam, Pongal) for culturally relevant campaigns.
Brand Manager Responsibilities for Indian Market
Managing brands in India presents unique challenges and opportunities
Regional Adaptation
India isn’t one market—it’s 28+ markets with different languages, cultures, and consumer behaviors. Brand managers must:
- Adapt messaging and creative for regional relevance while maintaining brand essence
- Use regional languages in campaigns for deeper connection
- Understand local cultural nuances and sensitivities
- Work with regional influencers and media
Multi-Channel Integration
Indian consumers interact with brands across traditional and digital channels:
- TV remains powerful for mass reach, especially in Tier 2/3 cities
- Digital channels dominate urban youth
- Print media still relevant for certain demographics
- Outdoor advertising effective in high-traffic areas
- E-commerce platforms are crucial brand touchpoints
Brand managers orchestrate consistent experiences across all these channels.
Competitive Intensity
Most categories in India have fierce competition—from global giants to scrappy local players:
- Continuous competitive monitoring
- Quick response to competitive threats
- Finding differentiation in crowded markets
- Defending market share while growing
Price-Value Balance
Indian consumers are value-conscious across income segments:
- Positioning must clearly communicate value, not just premium features
- Juggling affordability with quality perception
- Managing brand extensions at different price points
- Competing with unorganized sector offering lower prices
Brand Manager vs. Other Marketing Roles
Understanding how brand managers differ from related roles
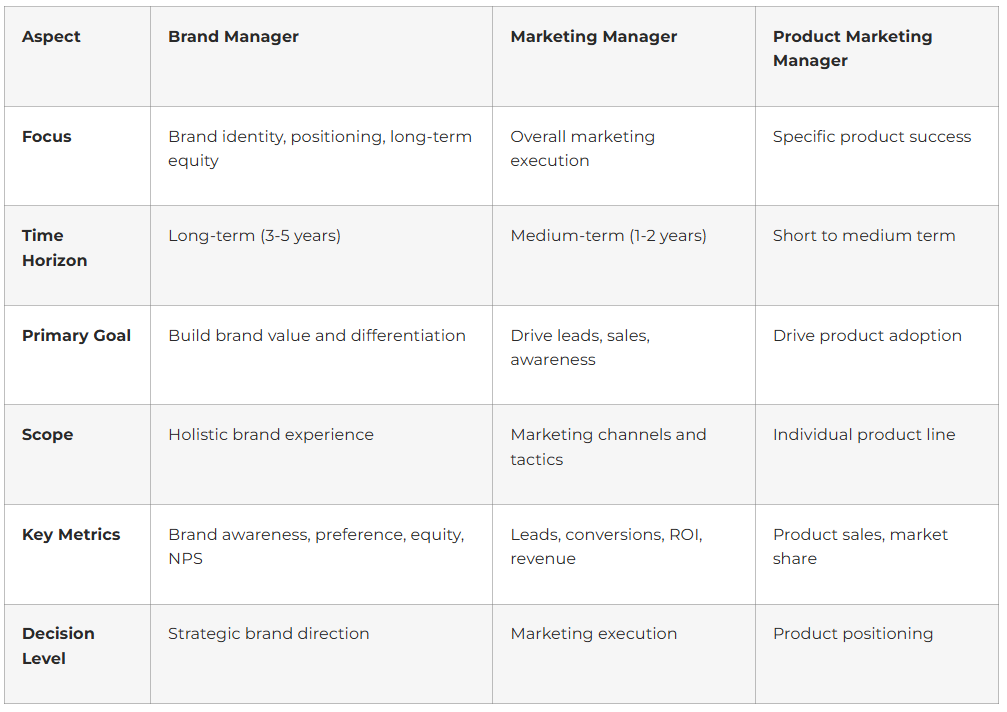
Brand managers typically have more strategic influence and broader scope compared to channel-specific marketers.
Brand Manager Salary in India
Brand managers command strong salaries reflecting their strategic importance:
Experience-Based Salary Ranges
- Assistant Brand Manager (0-3 years): ₹4-8 lakhs per year
- Brand Manager (3-6 years): ₹8-15 lakhs per year
- Senior Brand Manager (6-10 years): ₹15-25 lakhs per year
- Brand Lead/Associate Director (10+ years): ₹25-40 lakhs per year
Industry Variations
FMCG (Fast-Moving Consumer Goods): ₹8-30 lakhs
- Highest-paying industry for brand managers
- Companies like HUL, P&G, ITC, Marico pay premium salaries
- Strong brand management culture and training
Retail and E-commerce: ₹6-22 lakhs
- Brands like Flipkart, Amazon, Myntra, Ajio
- Fast-paced environment with digital-first approach
Technology and SaaS: ₹7-25 lakhs
- B2B and B2C tech brands
- Emphasis on positioning and differentiation
Automobile: ₹7-24 lakhs
- Car, two-wheeler, and commercial vehicle brands
- Long sales cycles requiring sustained brand building
Banking and Financial Services: ₹8-26 lakhs
- Banks, insurance, fintech companies
- Trust and credibility crucial in brand building
City-Wise Comparison
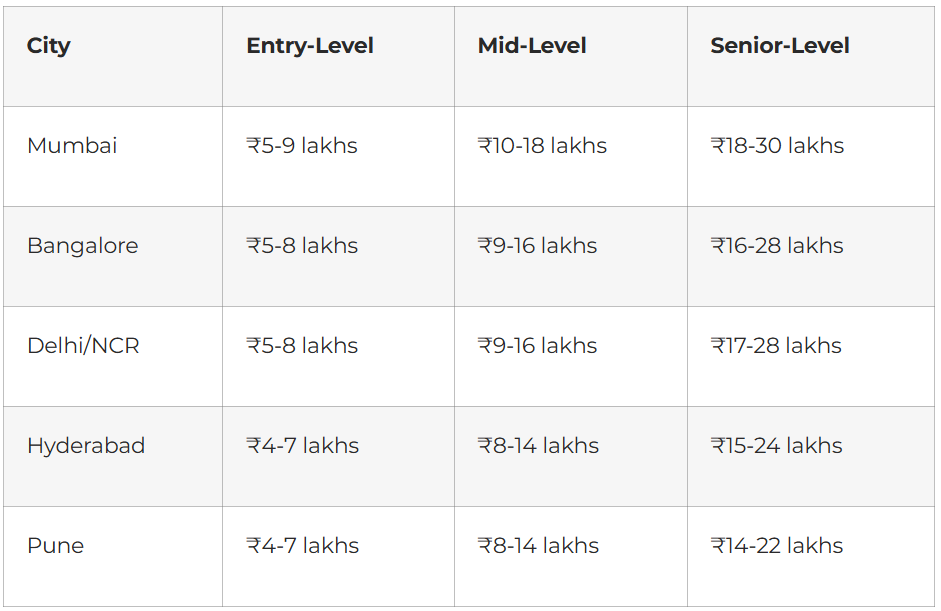
Mumbai offers highest salaries due to concentration of FMCG and consumer goods companies headquarters.
How to Become a Brand Manager
Educational Foundation
Ideal Academic Background:
- MBA in Marketing from reputed institutions (IIMs, XLRI, FMS, NMIMS, Symbiosis)
- Bachelor’s degree in marketing, business administration, communications, or related fields
- Many successful brand managers also come from engineering, science, or liberal arts backgrounds
Alternative Paths:
- Start in other marketing roles (digital marketing, content marketing, product marketing)
- Transition after 3-5 years of marketing experience
- Take specialized brand management courses or certifications
Year 1-3: Build Marketing Foundation
Start in Entry-Level Marketing Roles:
- Digital Marketing Executive
- Marketing Coordinator
- Product Marketing Executive
- Market Research Analyst
- Assistant Brand Manager (for MBA graduates)
Focus on Learning:
- Understand how marketing works across channels
- Develop analytical skills working with campaign data
- Learn consumer research methodologies
- Build presentation and communication skills
- Work on integrated campaigns to see big picture
Year 3-5: Develop Brand Thinking
Expand Responsibilities:
- Take ownership of smaller brands or product lines
- Lead campaign planning and execution
- Conduct market research and competitive analysis
- Work cross-functionally with sales, product, creative teams
- Manage budgets and vendor relationships
Key Skills to Develop:
- Strategic thinking beyond tactical execution
- Long-term planning and brand positioning
- Storytelling and creative briefing
- Stakeholder management and influencing skills
- Budget management
Year 5+: Move into Brand Manager Role
Typical Entry Points:
- Assistant Brand Manager → Brand Manager (FMCG route)
- Senior Marketing Executive → Brand Manager (other industries)
- Product Marketing Manager → Brand Manager (tech companies)
Build Your Brand Management Portfolio:
Project 1: Brand Strategy Document
- Choose existing brand and create comprehensive strategy
- Include: situation analysis, consumer insights, positioning, messaging architecture, channel strategy
- Present professionally with frameworks like SWOT, perceptual maps
Project 2: Campaign Case Study
- Document integrated campaign you worked on or create hypothetical one
- Show strategic thinking, creative development, execution plan, metrics
- Demonstrate ROI and brand impact
Project 3: Competitive Brand Analysis
- Analyze 3-4 competing brands in one category
- Compare positioning, messaging, target audiences, strengths/weaknesses
- Identify opportunities for differentiation
Project 4: Brand Repositioning Proposal
- Select brand needing repositioning
- Diagnose current perception issues
- Propose new positioning with rationale
- Create repositioning roadmap
Brand Management Frameworks to Master
Brand Positioning Framework
Classic positioning statement structure:
“For [target audience], [brand] is the [category] that [unique benefit/point of difference] because [reason to believe].”
Example: “For urban millennials seeking authentic experiences, XYZ Travel is the adventure travel company that creates transformative journeys because we focus on local immersion and sustainable tourism.”
Brand Essence Framework
Brand Pyramid:
- Attributes (base): Product features and characteristics
- Benefits: Functional and emotional benefits delivered
- Values: What the brand believes in
- Personality: If brand were a person, what traits would it have?
- Essence (top): Single-minded core idea capturing brand’s soul
Consumer Insight Development
Framework:
- Observation: What are consumers doing/saying?
- Tension: What’s the unmet need or frustration?
- Insight: The “aha!” understanding of underlying motivation
- Opportunity: How can the brand address this?
Example:
- Observation: Parents buy expensive learning toys
- Tension: Guilt about not spending enough quality time with kids
- Insight: Parents want to feel they’re good parents even when busy
- Opportunity: Position brand as enabling quality family moments
4 Ps of Marketing Mix
- Product: What are you selling?
- Price: What does it cost?
- Place: Where/how is it available?
- Promotion: How do you communicate about it?
Brand managers ensure all 4 Ps align with brand positioning.
Career Growth Path for Brand Managers
Year 0-3: Marketing Executive/Assistant Brand Manager
Execute marketing plans, support campaign implementation, conduct market research, coordinate with agencies. Expected salary: ₹4-8 lakhs.
Year 3-6: Brand Manager
Own brand strategy for product line or smaller brand, lead campaign development, manage budgets, present to senior management. Expected salary: ₹8-15 lakhs.
Year 6-10: Senior Brand Manager
Manage flagship brands or multiple brands, lead teams of 2-4 people, shape long-term brand strategy, larger budget responsibility. Expected salary: ₹15-25 lakhs.
Year 10-15: Brand Lead/Associate Director
Oversee brand portfolio, manage senior brand managers, shape category strategy, collaborate with business leadership. Expected salary: ₹25-35 lakhs.
Year 15+: Marketing Director/CMO
Lead entire marketing organization, set company marketing vision, report to CEO, major P&L responsibility. Expected salary: ₹35-75+ lakhs.
Alternative paths:
- Category Manager: Focus on entire product category
- Marketing Consultant: Advise multiple brands as external consultant
- Entrepreneur: Start own brand or marketing agency
Common Brand Management Challenges
Challenge 1: Measuring Brand Impact
Brand building effects are long-term and hard to attribute directly to specific activities.
Solution: Use brand tracking studies measuring awareness, consideration, preference over time. Combine with econometric modeling showing correlation between brand health and sales.
Challenge 2: Balancing Short-Term Sales vs. Long-Term Brand Building
Pressure to deliver immediate sales often conflicts with brand-building investments.
Solution: Allocate budget between brand building (60%) and sales activation (40%). Educate stakeholders that sustainable growth requires both.
Challenge 3: Maintaining Consistency Across Touchpoints
With multiple channels and teams, keeping brand experience consistent is challenging.
Solution: Create comprehensive brand guidelines, conduct regular training, establish approval processes, audit implementation.
Challenge 4: Competing with Price-Focused Competitors
Price warriors can undercut branded products, tempting brands to discount.
Solution: Strengthen brand differentiation beyond price, communicate value clearly, resist frequent discounting that erodes brand perception.
Challenge 5: Staying Relevant to Evolving Consumers
Consumer preferences, especially among youth, change rapidly.
Solution: Continuous consumer research, stay curious about cultural trends, test and learn approach, refresh brand without losing core essence.
FAQs: Brand Manager Career
Q: Do I need an MBA to become a brand manager?
Not mandatory but helpful. FMCG companies typically prefer MBA graduates. Tech, startups, and smaller companies hire based on experience and demonstrated skills regardless of MBA.
Q: What’s more important—creativity or analytical skills?
Both equally. Brand management requires creative storytelling combined with data-driven decision making. You need both right and left brain thinking.
Q: How long does it take to become a brand manager?
Typically 3-6 years of marketing experience. MBA graduates can start as Assistant Brand Managers and become Brand Managers in 2-3 years.
Q: Which industry offers best brand management careers?
FMCG offers most structured brand management training and highest salaries. Tech and e-commerce offer faster career progression but less formal brand management culture.
Q: Can I transition to brand management from other roles?
Yes. Many brand managers start in digital marketing, content marketing, product marketing, or market research then transition after demonstrating strategic thinking.
Your Next Steps: Start Your Brand Management Journey
Brand management is one of the most intellectually stimulating and impactful marketing careers. You’re not just running campaigns—you’re shaping how millions of people perceive and connect with brands. You’re building intangible assets worth crores that drive business success for decades.
If you’re currently in marketing, start thinking like a brand manager today. Look beyond your specific channel to the bigger brand picture. Ask yourself: “What should this brand stand for? How does my work contribute to long-term brand equity?” Volunteer for cross-functional projects. Build relationships across departments.
The brand managers earning ₹20-30 lakhs today started as marketing executives wondering how to make the jump to strategy. They developed brand thinking one project at a time, sought mentorship, and proved they could think beyond tactics to strategy. Your brand management career starts with shifting your mindset from executor to strategist.
