B.Ed After Graduation: Eligibility, Entrance Exams & Career Options
Table of Contents
Part 1: Understanding B.Ed - Why Pursue It After Graduation
Introduction
You’ve completed your Bachelor’s degree. Now what? If teaching interests you, B.Ed (Bachelor of Education) is typically the required next step. But is it worth 2 years and ₹1-5 lakhs investment? Will it lead to viable career? How does it compare to jumping directly into teaching?
B.Ed is India’s gateway to formal teaching profession. Without it, securing teaching positions in reputed schools, government posts, or international schools becomes nearly impossible. Yet many graduates hesitate—the 2-year investment feels long, the curriculum feels theoretical, and they wonder if they could just teach without formal certification.
This guide answers definitively: What B.Ed is, why it matters, who should pursue it, realistic career outcomes, and how to maximize your return on this investment.
What is B.Ed?
B.Ed (Bachelor of Education) is a 2-year post-graduation professional degree that trains you to teach in schools (Grades 1-12). It’s distinct from B.A., B.Sc., B.Com. (which are knowledge degrees) and vocational degrees (which teach skills). B.Ed is a pedagogy degree—it teaches HOW to teach, not just subject knowledge.
B.Ed curriculum typically includes:
- Educational psychology and child development
- Pedagogy (teaching methodologies)
- Curriculum design
- Assessment and evaluation
- Subject-specific teaching methods (varies by specialization)
- Practice teaching (internship in schools)
- Educational technology
- Inclusive education
- Research methods
Duration: 2 years (4 semesters)
- Year 1: Theory + foundational practice
- Year 2: Specialized subject training + extensive school internship (6-8 weeks minimum)
Specializations available:
- English, Mathematics, Science, Social Studies (single subject)
- Combinations: English + Social Studies, Math + Science, etc.
- Special Education
- Physical Education
- Commerce, Economics
Why Pursue B.Ed After Graduation?
Reason 1: Teaching Career Requirement
B.Ed is mandatory for formal teaching in India. Without it:
- ❌ Cannot get government teaching jobs
- ❌ Cannot teach in reputed private schools
- ❌ Cannot teach in international schools (usually requires it)
- ❌ Cannot attempt UGC NET (for lecturer positions)
B.Ed is THE credential that opens teaching doors. Your subject knowledge (Bachelor’s degree) is prerequisite, but B.Ed is permission slip to teach.
Reason 2: Pedagogical Skills
Subject knowledge ≠ Teaching ability. B.Ed teaches:
- How students learn (learning theories)
- How to explain complex concepts simply
- How to manage diverse classrooms
- How to assess student learning effectively
- How to use technology in teaching
- How to support struggling learners
A PhD in Physics doesn’t make you good teacher; B.Ed training does. B.Ed is the difference between knowing subject and teaching it effectively.
Reason 3: Government Teaching Jobs
Government school positions (most secure, permanent jobs in India) require B.Ed. Typically:
- Bachelor’s degree (any subject)
- B.Ed qualification
- Pass state TET/CTET exam
- Interview
- → Government teaching position with permanent job security
Without B.Ed, entire government pathway (millions of positions) is closed.
Reason 4: Career Progression
B.Ed enables:
- Teaching at primary, secondary, senior secondary levels
- Leadership roles (department head, principal)
- Educational administration
- Curriculum development
- Teacher training
- Higher education (if pursuing Master’s/PhD)
Reason 5: Competitive Edge
In job market:
- Without B.Ed: Compete only for unqualified tutoring
- With B.Ed: Access entire teaching industry
- With B.Ed + certifications (IB, CELTA): Access premium roles
B.Ed multiplies your career options exponentially.
The Hard Truth: What B.Ed Won't Do
Before investing, understand limitations:
❌ B.Ed won’t guarantee job
Many B.Ed graduates struggle finding placements. Quality of B.Ed program varies drastically. Some top programs have 95% placements; others have 40%. Choosing right college matters enormously.
❌ B.Ed won’t make you rich
Teaching salaries in India are modest (₹3-6 lakhs entry, ₹8-12 lakhs experienced). If primary goal is wealth, consider other careers first.
❌ B.Ed won’t happen quickly
2 years is long commitment. If you need income immediately, consider other options.
❌ B.Ed curriculum is sometimes theoretical
Many B.Ed programs are academic rather than practical. Lectures on “theories of learning” feel removed from real classrooms. Quality varies.
❌ B.Ed doesn’t guarantee specific school placement
You get qualification, not job promise. You must then apply to schools, interview, and compete.
Who SHOULD Pursue B.Ed?
Perfect candidates:
✅ You’re passionate about teaching
If you genuinely enjoy explaining concepts, helping others learn, mentoring students—B.Ed channels this passion into profession.
✅ You want job security
If financial security matters (vs. wealth), teaching offers permanence. B.Ed enables this path.
✅ You’re interested in education systemically
If you wonder how education works, how to improve learning, what curriculum should be—B.Ed explores these deeply.
✅ You’re not pursuing immediate high income
If you’re okay with modest salary, teaching is viable path. B.Ed is investment in meaningful career, not get-rich-quick.
✅ You want work-life balance
Teaching offers holidays (2 months summer, festivals). It’s lifestyle choice, enabled by B.Ed qualification.
✅ You’re considering government job
If security and pension matter, government teaching is excellent. B.Ed is essential requirement.
Who SHOULD NOT Pursue B.Ed (Yet)
❌ You’re undecided about teaching
Don’t invest 2 years if uncertain. Take time, volunteer in schools, try tutoring first. If you still love it, do B.Ed.
❌ You need immediate income
B.Ed takes 2 years before employment. If you need money now, work first, then pursue B.Ed.
❌ Your primary goal is high income
If wealth is priority, teaching isn’t path. Pursue engineering, management, business instead. Then reconsider teaching as second career later.
❌ You’re pursuing B.Ed as backup plan
“If nothing else works, I’ll teach” is wrong motivation. Teaching requires genuine commitment. B.Ed with wrong motivation is wasted investment.
B.Ed vs. Other Post-Graduation Options

Key comparison:
- B.Ed: Modest salary, high job security, meaningful work, good work-life balance
- MBA: Higher salary, lower security, competitive environment
- M.Tech: Highest salary, high security (IT demand), technical path
- No further study: Immediate income, limited progression
B.Ed is best choice if: Security + Meaning > Salary + Prestige
Part 2: B.Ed Eligibility, Entrance Exams & Admission Process
B.Ed Eligibility Criteria
Basic eligibility (All India):
- ✅ Bachelor’s degree (Any discipline: B.A., B.Sc., B.Com., etc.)
- ✅ Minimum 50% marks in Bachelor’s (sometimes 45% for reserved categories)
- ✅ Any subject specialization works (Physics graduate can teach English if B.Ed in English)
No eligibility:
- ❌ Diploma holders (they pursue D.Ed instead)
- ❌ Candidates without Bachelor’s degree
- ❌ Below cutoff percentage (varies by state)
Age limit: Typically none (unlike some competitive exams)
Example eligibility scenario:
“I completed B.Sc. in Physics with 55% marks. Can I pursue B.Ed?”
Answer: YES! You have Bachelor’s degree + 50%+ marks. You can pursue B.Ed in any subject (Physics, Mathematics, English, etc.). Your Physics degree is bonus; B.Ed training makes you teacher.
B.Ed Entrance Exams in India
Different states conduct different entrance exams for B.Ed admission. Major exams:
National-level entrance exams:
- CUET (Common University Entrance Test) – UG
- Conducted by: National Testing Agency (NTA)
- Applicable: Central Universities + some state universities
- Eligibility: Bachelor’s degree with 50%+ marks
- Pattern: Multiple choice questions (MCQs)
- Coverage: General knowledge, aptitude, subject-specific
- Validity: Nationwide accepted
- State-level entrance exams:

- University-specific entrance exams:
- Some universities conduct their own entrance exams
- Example: Delhi University B.Ed entrance, Osmania University B.Ed entrance
Which exam should you take?
- If targeting Central University (Delhi, Mumbai, etc.): CUET
- If targeting state university: State entrance exam
- If targeting private university: University’s entrance exam
- You can appear in multiple exams simultaneously
B.Ed Entrance Exam Preparation
Typical exam pattern:

Sample question types:
Reasoning: “If all teachers are educators, and some educators are researchers, are all teachers researchers?” Answer: Cannot be determined.
General Knowledge: “Who is current Education Minister of India?” Answer: [Current minister name]
Teaching Aptitude: “A student isn’t understanding a concept. As teacher, your first step is?” Options: a) Move to next topic b) Diagnose root cause c) Give more homework d) None
Answer: b) Diagnose root cause (shows pedagogical understanding)
Preparation strategy:
- Duration: 2-4 months sufficient
- Study time: 1-2 hours daily
- Focus areas: Reasoning (30%), GK (25%), subject (25%), teaching aptitude (20%)
- Resources: Books, online courses, mock tests
- Mock tests: Attempt 10+ full-length tests before exam
B.Ed Admission Process (State-wise Example: Telangana)
Step 1: Online Application (June)
- Candidate fills online form on EDCET website
- Provides: Personal details, Bachelor’s marks, subject preference
- Pays: Application fee ₹500-800
Step 2: Entrance Exam (July)
- Exam conducted in test centers
- Pattern: MCQ-based, 2-3 hours duration
- Questions: General knowledge, subject, aptitude, English
Step 3: Result Declaration (August)
- Results published within 1-2 weeks
- Scorecard downloadable
- Merit list released
Step 4: Counselling (August-September)
- Candidates called for counselling in merit order
- Choose college preference
- Seat allocated based on merit + choice + college availability
Step 5: Admission (September)
- Report to allocated college
- Complete verification
- Pay fees
- Enroll in B.Ed program
Timeline (Example):
- June: Application
- July: Entrance exam
- August: Results + counselling
- September: Admission + program start
- Total process: 4 months
B.Ed Admission Without Entrance Exam
Some institutions offer direct admission based on merit:
Merit-based admission:
- Bachelor’s marks: Minimum 50-55%
- No entrance exam needed
- Direct counselling and seat allocation
- Usually private colleges
When to choose merit-based:
✅ If entrance exam stress is high
✅ If you’re confident in Bachelor’s performance
✅ If you prefer direct admission timeline
Caution: Merit-based institutions sometimes have lower standards. Choose carefully—college quality significantly impacts your learning and placements.
Part 3: B.Ed Colleges, Fees & Career Outcomes
Top B.Ed Colleges in India
Tier 1: Premier Central Universities

Tier 2: Good State Universities

Tier 3: Private B.Ed Colleges

How to choose college:
✅ Research placement records
- Ask previous batch placements
- Check employer companies
- Understand average salary offered
✅ Visit campus
- Meet current students
- Assess infrastructure
- Check library, labs, teaching materials
✅ Evaluate faculty
- Faculty qualifications and experience
- Student-faculty ratio
- Research orientation
✅ Consider location
- Urban locations: Better placements
- Small cities: Lower fees, focused learning
- Your preference: Where you want to teach
✅ Balance cost vs. quality
- Government college: Cheaper (₹30-50K), respected, merit-based
- Private college: Expensive (₹2-5L), variable quality, easier admission
- Sweet spot: Good government college (best value)
B.Ed Fees Breakdown
Government College (2-year total):
- Tuition fees: ₹20,000-40,000
- Exam fees: ₹5,000-10,000
- Activities/resources: ₹10,000-15,000
- Total: ₹35,000-65,000 (Roughly ₹3-5 lakhs per year)
Private College (2-year total):
- Tuition fees: ₹1.5-2.5 lakhs/year
- Infrastructure: ₹50,000-1 lakh/year
- Activities/resources: ₹25,000-50,000/year
- Total: ₹2-5 lakhs per year = ₹4-10 lakhs for 2 years
Optional expenses:
- Books and materials: ₹10,000-20,000
- Internship travel: ₹10,000-30,000
- Certifications (optional): ₹20,000-50,000
- Accommodation (if hostel): ₹1-2 lakhs/year
Scholarship opportunities:
- Government scholarships: SC/ST candidates often get ₹50-100% fee waiver
- Merit scholarships: Top scorers may get ₹10-50% reduction
- State scholarships: Many states offer scholarships for B.Ed
- Seek before admission to reduce financial burden
Integrated B.A./B.Sc. + B.Ed Programs
What is integrated program?
Rather than Bachelor’s (3 years) + B.Ed (2 years) = 5 years separately, integrated program combines them into 4 years:
- Year 1-2: General Bachelor’s courses + foundational education theory
- Year 3-4: Specialized courses + practice teaching
Duration: 4 years (vs. 5 years separately)
Cost: ₹2-4 lakhs (vs. ₹6-8 lakhs separately)
Outcome: B.A./B.Sc. + B.Ed both degrees
Advantages:
✅ 1 year time saving
✅ Lower total cost
✅ Integrated learning (subject + pedagogy together)
✅ Immediate job-ready after 4 years
Disadvantages:
❌ Less flexibility (commitment to teaching from start)
❌ Fewer college options than standalone programs
❌ Fewer specialization options
Best for:
- Students certain about teaching career
- Those wanting time/cost efficiency
- School leavers (12th pass) → Integrated 4-year program
Colleges offering integrated programs:
- Banaras Hindu University (BHU)
- Aligarh Muslim University (AMU)
- Shobhit University
- Lovely Professional University
- Several state universities
B.Ed Career Options & Placements
Immediate post-B.Ed career options:
- School Teaching (Primary path)
- Government schools: ₹3-5 lakhs/year, permanent job
- Private schools: ₹4-8 lakhs/year, contract-based
- International schools: ₹8-15 lakhs/year, higher standards
- Online tutoring: ₹3-10 lakhs/year, flexible
- Educational Administration
- Curriculum coordinator
- Academic advisor
- Educational NGO roles
- ₹5-10 lakhs/year
- Special Education
- Special schools
- Inclusive education roles
- ₹6-12 lakhs/year
- Often high demand
- Further Education (Master’s degree)
- M.Ed (Master’s in Education): 2 years
- Path to: Educational research, university teaching, policy roles
- Investment: ₹1-3 lakhs
- Payoff: ₹8-15 lakhs/year after M.Ed
- EdTech & Online Learning
- Content creation
- Curriculum development
- Online tutoring platforms
- ₹8-20 lakhs/year
- Growing sector
Realistic Placement Statistics 2025
Data from top B.Ed colleges:
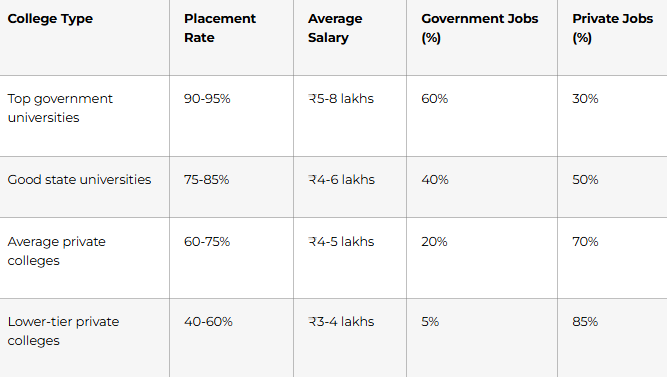
Key insights:
- College quality matters enormously. Top college → 95% placement at ₹6-8L. Lower college → 60% placement at ₹3-4L.
- Government jobs highly competitive. Only top 30-40% of graduates get government positions. Others pursue private/international/online.
- Most get jobs, but quality varies. Even “low placement rate” colleges (60%) place most graduates; it’s job quality that differs.
Example scenarios:
Scenario A: Top college graduate
- Placement rate: 95%
- Likely path: 60% get government job at ₹4.5L (secure), 30% private school at ₹6L
- Average salary: ₹5-6 lakhs
- Job security: High
Scenario B: Average college graduate
- Placement rate: 70%
- Likely path: 20% government job, 70% private school, 10% online
- Average salary: ₹4-5 lakhs
- Job security: Moderate
Scenario C: Lower-tier college graduate
- Placement rate: 50%
- Likely path: 5% government job, 75% private school, 20% online/other
- Average salary: ₹3-4 lakhs
- Job security: Lower
How B.Ed Leads to Government Teaching Jobs
Government job pathway:
text
B.Ed Graduation (June)
↓
Pass State TET/CTET exam (July-September)
↓
Wait for vacancy announcements (Varies, 3-12 months)
↓
Apply for advertised positions
↓
Interview (if shortlisted)
↓
Document verification
↓
Offer letter + joining
↓
Government teacher (permanent, ₹3-5L/year, pension)
Timeline: 1-2 years from B.Ed completion to government job
Competitive reality: Of B.Ed graduates:
- 50% ultimately secure government job
- 30% continue searching or pursue private sector
- 20% transition to EdTech/other careers
This is why: Government jobs are limited (finite positions), competitive (many applicants), and time-consuming (selection process takes months/years).
Part 4: Making B.Ed Decision - Action Steps
Should You Pursue B.Ed? Decision Checklist
Answer honestly:
- Passion for teaching?
- ❌ No → Don’t pursue (you’ll regret 2 years)
- ✅ Yes → Continue
- Comfortable with modest salary?
- ❌ Need high income → Consider other careers first
- ✅ Okay with ₹5-10 lakhs → Continue
- Want job security?
- ❌ Prefer flexibility/entrepreneurship → Other paths better
- ✅ Value stability → B.Ed is good choice
- Have 2 years to invest?
- ❌ Need immediate income → Work first, B.Ed later
- ✅ Can spare 2 years → Continue
- Bachelor’s degree with 50%+ marks?
- ❌ Below cutoff → Get extra qualification first
- ✅ Yes → Eligible
If you answered ✅ to all 5: B.Ed is right path for you.
Action Plan: Before Applying to B.Ed
Month 1: Research
✅ Visit 5-10 B.Ed colleges
✅ Talk to current B.Ed students
✅ Understand entrance exams in your state
✅ Research government job prospects in your region
✅ Clarify: Is teaching truly your passion?
Month 2: Preparation
✅ Enroll in entrance exam coaching (if needed)
✅ Start daily study: 1-2 hours
✅ Take mock tests
✅ Finalize college choices (3-5 colleges)
Month 3-4: Application & Exam
✅ Complete online applications
✅ Pay application fees
✅ Appear for entrance exam
✅ Await results
Month 5-6: Counseling & Admission
✅ Attend counselling sessions
✅ Choose college based on merit + preference
✅ Complete admission formalities
✅ Pay fees
✅ Join B.Ed program
B.Ed Application Timeline
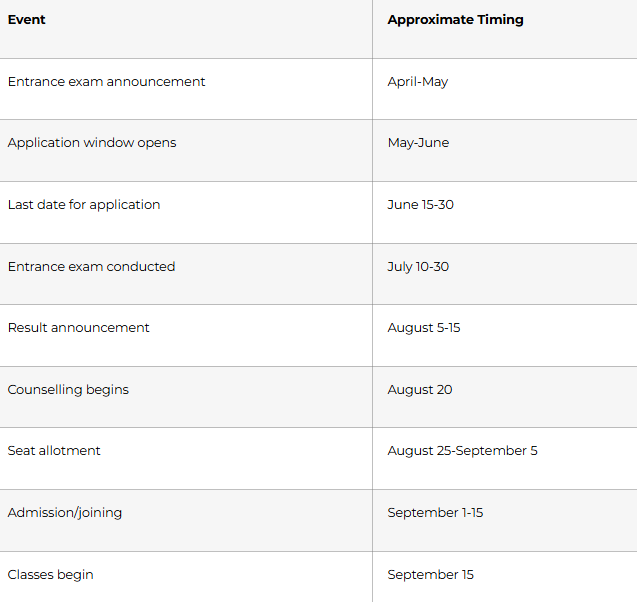
Pro tip: Mark dates in calendar 6 months in advance. B.Ed cycles have fixed timeline; missing dates means missing year.
Red Flags: Bad B.Ed Colleges to Avoid
Exercise 1: The 30-60-90 Second Drill
🚨 Warning signs:
- ❌ Extremely low fees with poor infrastructure (likely unrecognized)
- ❌ 0% placement data or unavailable information
- ❌ Faculty without qualification or experience
- ❌ No school partnerships for internship
- ❌ Poor online reputation or negative reviews
- ❌ No library or limited resources
- ❌ Classes in rented buildings (unstable)
- ❌ No alumni network or career support
Before enrolling: Verify college accreditation, recognition, NAAC rating.
B.Ed Success Metrics: How to Maximize Value
Once enrolled in B.Ed, ensure you get maximum value:
✅ Choose subject wisely
- Choose subject you can teach well, not just like
- High-demand subjects: English, Math, Science
- Easier to place with these
✅ Excel in practice teaching
- This is most important for hiring
- Your school internship determines first job often
- Perform exceptionally here
✅ Build teaching portfolio
- Create lesson plans, assessments, teaching materials
- Show during interviews
- Portfolio impresses employers
✅ Get additional certifications
- Google Educator, TESOL, IB (if possible)
- These add huge value to resume
- Available during/after B.Ed
✅ Network with educators
- Join teacher communities
- Attend education seminars
- Build connections for job opportunities
✅ Pursue government job systematically
- After B.Ed, immediately prepare for TET/CTET
- Attempt exam while in final semester if possible
- Don’t wait; competition is fierce
✅ Consider education M.Ed if ambitious
- M.Ed after B.Ed → Leadership roles
- 2 additional years → ₹8-15 lakhs/year income potential
- Worth it if you want senior roles
Complete B.Ed Decision Framework
Decision tree:
text
Question: Do you want to teach?
YES → Continue
NO → Consider other careers
Question: Are you passionate about education?
YES → Continue
NO → Maybe revisit later
Question: Can you invest 2 years?
YES → Continue
NO → Work first, then B.Ed
Question: Are you okay with modest starting salary (₹3-5L)?
YES → Continue
NO → Consider high-income careers first
Question: Do you value job security?
YES → B.Ed is excellent choice
NO → Consider entrepreneurship or corporate careers
Question: Bachelor’s degree with 50%+ marks?
YES → Eligible for B.Ed
NO → Improve marks or wait for admission
→ RESULT: If all YES → Pursue B.Ed with confidence
→ If multiple NO → Reconsider; teaching may not be right path currently
Final Perspective on B.Ed
B.Ed is investment, not expense.
A ₹3-5 lakh investment in 2 years leads to:
- Immediate teaching career (₹3-5 lakhs/year) or
- Government job pathway (₹4-6 lakhs/year + pension) or
- Further education enabling (M.Ed, leadership roles, ₹15-25 lakhs/year)
Over 30-year career:
- ₹3-5L investment → ₹1.5-2 crore cumulative earnings
- ROI: 3000-4000% return over career lifespan
That’s exceptional return on investment for relatively small upfront cost.
The real question isn’t “Is B.Ed worth it?” but “Am I truly passionate about teaching?”
If yes to passion, B.Ed is absolutely worth it. If no to passion, no investment amount makes it worthwhile.
