Environmental Science Courses in India: BSc, MSc, BTech & Career Path
Table of Contents
Introduction
If you care about pollution, climate change, forests, and clean water, but also want a stable career, environmental science can be a strong choice. It connects subjects like biology, chemistry, geography, and technology to solve real-world problems such as air pollution, water contamination, waste, and biodiversity loss.
This guide walks you through all major education options in India—after 10th, after 12th, after graduation, and even options for working professionals—using simple language so students and parents can understand and plan clearly.
1. What Is Environmental Science as a Course?
Environmental science is an interdisciplinary subject that studies the relationship between humans and the environment using knowledge from biology, chemistry, physics, geology, and social sciences.
Typical topics covered include:
- Pollution (air, water, soil, noise) and control methods.
- Ecology and ecosystems.
- Environmental chemistry and toxicology.
- Natural resource management (water, forests, minerals, biodiversity).
- Climate change and environmental policies.
Unlike pure science subjects that stay mostly in labs or theory, environmental science is strongly application-focused, linking your classroom learning directly to issues you see in the news and in your city or village.
2. After Class 10: Choosing the Right Stream
Your stream in 11th–12th does not fully decide your future, but it does make certain paths easier.
Best Stream for Environmental Science
- Science (PCB or PCMB) is the most flexible choice if you want to keep open options for:
- BSc Environmental Science, Life Sciences, Zoology, Botany, Geology.
- BTech Environmental or Civil Engineering with environmental focus.
- BSc Environmental Science, Life Sciences, Zoology, Botany, Geology.
Science gives a strong base in physics, chemistry, and biology, which are used heavily in environmental degrees and careers.
Can Arts or Commerce Students Enter Environmental Fields?
Yes, but usually through:
- BA/BSc in Environmental Studies, Geography, or related subjects.
- Later, master’s degrees in Environmental Management, Sustainability, or an MBA in Sustainability.
So, Science stream makes the journey simpler, but Arts/Commerce can still lead into certain environmental and sustainability roles with careful planning.
3. After Class 12: Main Environmental Degree Options
3.1 BSc Environmental Science (3 Years)
Who it is for:
Students who like biology, basic chemistry, and want to understand pollution, ecosystems, and conservation in depth.
Common Eligibility (India):
- 10+2 with Science (usually PCB/PCM), minimum 50–60% (varies by college).
Typical Subjects:
- Fundamentals of Ecology and Environment.
- Environmental Chemistry and Toxicology.
- Environmental Pollution and Control.
- Environmental Laws and Policies.
- Biodiversity and Conservation.
- Practical work: sampling, basic lab work, field visits.
Pros:
- Strong conceptual foundation in environment.
- Opens doors to MSc and a wide range of entry-level environmental roles.
- Good fit for those interested in research, monitoring, conservation, or consulting support roles.
Career Options After BSc:
- Environmental technician or field assistant.
- Junior analyst in environmental labs.
- Assistant in environmental consulting firms.
- NGO roles in environmental projects and awareness programs.
Entry-level salaries often fall in the ₹3–6 LPA range depending on location and employer.
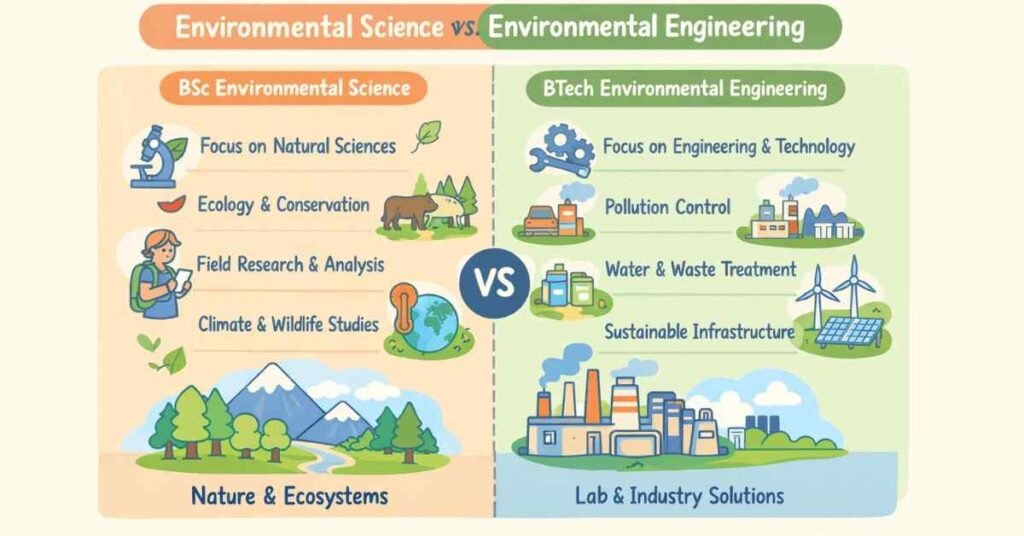
3.2 BTech / BE Environmental Engineering (4 Years)
Who it is for:
Students who enjoy maths and engineering and want to design treatment plants, pollution control systems, and other technical solutions.
Common Eligibility:
- 10+2 with PCM (Physics, Chemistry, Maths), often through JEE Main or state engineering entrance exams.
Typical Subjects:
- Fluid Mechanics, Engineering Mathematics.
- Water and Wastewater Engineering.
- Air Pollution Control Engineering.
- Solid and Hazardous Waste Management.
- Environmental Impact Assessment and Management.
Pros:
- Technical degree with strong demand in industries, infrastructure projects, and consulting.
- Good for roles like environmental engineer, EHS engineer, and treatment plant design consultant.
Career Options After BTech Environmental:
- Environmental Engineer in manufacturing, water, waste, or infrastructure companies.
- EHS Engineer/Officer in plants.
- Environmental consultant with more technical focus.
Salaries usually start around ₹4–8 LPA and can rise significantly with experience and sector choice.
3.3 Related BSc Degrees That Can Lead to Environmental Careers
If BSc Environmental Science isn’t available or you have a broader interest, you can choose:
- BSc Life Sciences, Zoology, Botany.
- BSc Geology or Earth Sciences.
- BSc Microbiology, Biochemistry (useful for pollution and water quality career paths).
Later, you can move into environment-focused master’s programs like MSc Environmental Science, Ecology, or Conservation.

3.4 BA/BSc Environmental Studies or Geography
For students from Arts/Commerce or those more interested in policy, planning, or social aspects:
- BA/BSc in Environmental Studies, Sustainable Development, or Geography can be a good foundation for environment-linked policy, planning, or community work.
- After graduation, you can pursue a master’s in Environmental Management, Urban Planning, or Sustainability.
4. Top-Level View: Notable Environmental Programs in India
Many central and state universities now offer environmental science and related programs. Typical examples include:
- Central universities and well-known state universities offering BSc/MSc Environmental Science and related courses.
- Engineering colleges including IITs, NITs, and state engineering colleges offering Environmental or Civil Engineering with environmental specializations.
Seats, fees, and entrance criteria vary, so students should always check the latest prospectus or official website for updated details.
5. After Graduation: MSc, MTech and MBA Options
Once you complete a bachelor’s degree, you can either start working or study further. Higher studies help you move into more specialized, higher-paying roles.

5.1 MSc Environmental Science / Environmental Management (2 Years)
Eligibility:
- BSc in Environmental Science or a related science discipline with required minimum marks (often 50% or above).
What You Study:
- Advanced environmental pollution control.
- Environmental impact assessment and risk analysis.
- Environmental law, policy, and governance.
- Climate change, sustainability, and resource management.
- Research methods and dissertation project.
Career Advantages:
- Qualify for more senior roles in labs, consulting, and policy.
- Competitive for positions such as environmental officer, senior analyst, or project manager in NGOs and companies.
5.2 MTech Environmental Engineering / Related Fields (2 Years)
Eligibility:
- BE/BTech in Environmental, Civil, Chemical, or related disciplines.
Focus Areas:
- Advanced wastewater and industrial effluent treatment design.
- Air quality modeling and control systems.
- Advanced solid and hazardous waste management.
- Environmental modeling and simulation.
Career Advantages:
- Senior technical roles in engineering firms, infrastructure projects, and high-end consulting.
- Roles in research and development or design teams.
5.3 MBA in Sustainability / Environmental Management / ESG
Eligibility:
- Any bachelor’s degree plus required entrance exam scores (CAT, MAT, etc.) based on institute.
What You Learn:
- Business and management fundamentals.
- Corporate sustainability, ESG, and responsible business strategies.
- Sustainable finance, climate risk, and sustainability reporting.
Career Advantages:
- Positions in corporate sustainability, ESG analysis, sustainability consulting, and CSR strategy.
- Combines environment interest with leadership and higher salary potential.
6. Diploma and Certificate Options (After 10th, 12th, or Graduation)
Not everyone wants or can pursue a full degree. Diplomas and certificates are useful for quick entry or for working professionals.
6.1 Diplomas (2–3 Years)
- Diploma in Environmental Science / Technology / Health & Safety:
- Offered by polytechnics or specialized institutes.
- Suitable for lab, field technician, or assistant roles.
- Offered by polytechnics or specialized institutes.
These can lead to jobs such as environmental technician, sample collector, or junior plant operator in water/waste facilities, with options for lateral entry into degrees in some institutions.
6.2 PG Diplomas and Part-Time Programs (6–24 Months)
- Postgraduate Diploma in Environmental Management / Sustainability / Environmental Health & Safety.
- Designed for graduates or working professionals who want to add environmental expertise without a full-time master’s.
6.3 Online Certificates
- Short courses in environmental science, climate change, sustainability, and ESG offered through global platforms and specialized institutes.
Ideal for skill-building (GIS, carbon accounting, environmental law basics, etc.).
7. Entrance Exams and Admissions
Day Before the Interview
Different programs use different entry routes:
- Engineering (BTech Environmental/Civil):
- JEE Main/Advanced or state engineering entrance exams in many colleges.
- JEE Main/Advanced or state engineering entrance exams in many colleges.
- BSc Environmental Science:
- Often merit-based using 12th marks; some universities use entrance exams (like CUET or institute-level tests).
- Often merit-based using 12th marks; some universities use entrance exams (like CUET or institute-level tests).
- MSc/MTech:
- Entrance exams or merit lists based on bachelor’s performance or a mix of both, depending on the university.
- Entrance exams or merit lists based on bachelor’s performance or a mix of both, depending on the university.
Students should always check current admission notifications, as patterns change over time.
8. Skills You Build During Environmental Courses
Well-designed environmental programs don’t just teach theory; they build practical and transferable skills.
Technical Skills
- Sampling and monitoring of air, water, and soil quality.
- Laboratory analysis techniques and standard methods.
- Use of GIS and remote sensing tools basics in some courses.
- Understanding environmental regulations and compliance requirements.
- EIA and risk assessment frameworks.
Soft and Professional Skills
- Report writing and documentation.
- Data analysis and presentation in Excel and basic statistical tools.
- Problem-solving and critical thinking on real environmental issues.
- Teamwork through group projects and fieldwork.
These skills are valuable not only for environmental jobs but also for general analytical, consulting, and project roles across sectors.
9. What Jobs Can You Get After Environmental Degrees?
Your exact role depends on your degree level and specialization, but common options include:
- After BSc Environmental Science:
- Environmental technician or monitoring staff.
- Junior environmental officer in small industries or local bodies.
- Research assistant or project assistant in environmental projects.
- Environmental technician or monitoring staff.
- After MSc Environmental Science / Management:
- Environmental scientist or analyst.
- Environmental consultant.
- Environmental officer in companies or infrastructure projects.
- Project manager in environmental NGOs.
- Environmental scientist or analyst.
- After BTech/MTech Environmental Engineering:
- Environmental engineer in design, projects, or plant operations.
- EHS engineer/manager.
- Technical consultant for pollution control, water/waste projects.
- Environmental engineer in design, projects, or plant operations.
- After MBA Sustainability / Environmental Management:
- Corporate sustainability manager.
- ESG or sustainability analyst.
- Sustainability or climate consultant.
- Corporate sustainability manager.
10. How to Choose the Right Course for You
Ask yourself a few simple questions:
- Do you enjoy biology and ecosystems more, or maths and engineering?
- Biology/ecosystem preference → BSc Environmental Science / Wildlife / Ecology.
- Maths/engineering preference → BTech Environmental or Civil with environmental focus.
- Biology/ecosystem preference → BSc Environmental Science / Wildlife / Ecology.
- Do you want to work more in technical/plant design, field/research, or corporate/strategy?
- Technical/plant → Environmental Engineering.
- Field/research → BSc/MSc Environmental Science, Ecology, Wildlife.
- Corporate/strategy → Combine environment degree with MBA or business-side skills for sustainability and ESG roles.
- Technical/plant → Environmental Engineering.
- How soon do you need to start earning?
- If very soon: consider diplomas or entry after bachelor’s.
- If you can invest more time: adding a master’s or MBA sharply improves your long-term options.
- If very soon: consider diplomas or entry after bachelor’s.
