Robotics Engineer—The Automation Designer
Table of Contents
From Technician to Engineer: The Strategic Leap
An automation technician installs and maintains robots. A robotics engineer designs and innovates robots. The difference: one follows existing solutions; the other creates new ones.
Robotics engineers earn ₹50,000-75,000/month as entry-level engineers, advancing to ₹1,00,000-1,80,000+/month within 8-10 years in senior roles. They lead the automation strategy for entire facilities. They design the robots of tomorrow.
What Robotics Engineers Actually Do:
Priya, Robotics Engineer at a manufacturing facility, faces a challenge: Assembly line is too slow. Current manual assembly: 200 units/day. Goal: 500 units/day with zero quality compromises.
Her solution: Design a robotic assembly system from scratch.
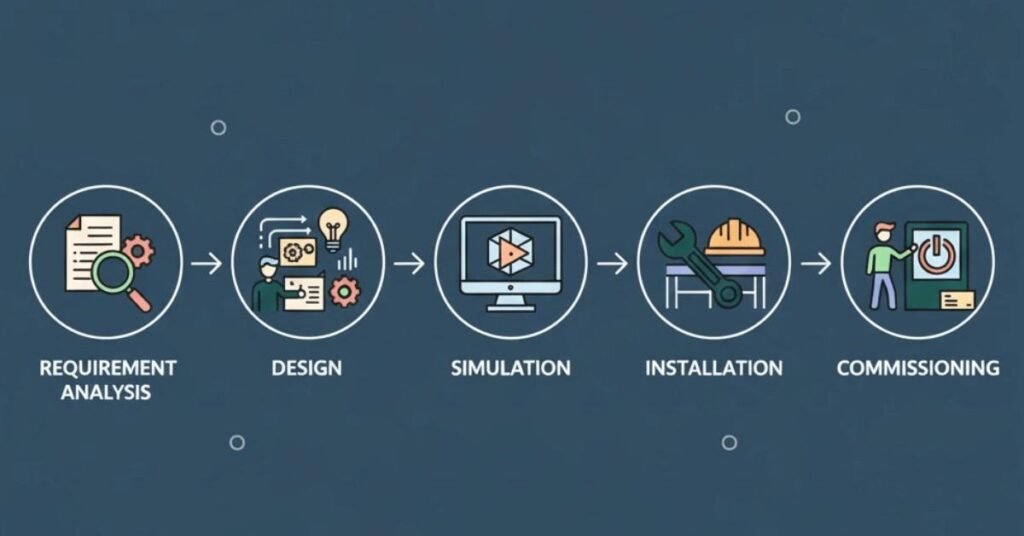
Phase 1: Requirement Analysis (Week 1-2)
- Studies the assembly process in detail
- Identifies which steps can be automated (assembly, placement, fastening)
- Determines precision requirements (tolerances needed)
- Calculates cycle time needed (to achieve 500 units/day)
- Estimates budget (₹1 crore for equipment)
- Evaluates available space (factory floor layout)
Phase 2: Conceptual Design (Week 3-4)
- Sketches robotic system layout using CAD
- Selects robot type (articulated arms, collaborative robots)
- Determines number of robots needed (simulation shows 3 robots handle the load)
- Designs end-effectors (grippers, tools) for specific assembly tasks
- Plans integration with conveyor, material handling systems
- Calculates ROI (₹1 crore investment saves ₹3 crore annually = 4-month payback)
Phase 3: Detailed Design (Week 5-8)
- Creates technical drawings using CAD/CAM software
- Designs safety systems (collision detection, emergency stops)
- Plans electrical and compressed air connections
- Designs material feeding systems (components reach robot at right time)
- Creates detailed specifications for procurement
- Documents all design decisions with reasoning
Phase 4: Simulation & Optimization (Week 9-12)
- Simulates robot movements in software (ensures feasibility)
- Tests cycle time in simulation (will it really achieve 500 units/day?)
- Identifies potential issues before hardware arrives
- Optimizes movements to reduce cycle time further (simulation shows 2.8 seconds/unit instead of 3 seconds)
- Verifies safety scenarios in simulation
- Plans training documentation
Phase 5: Implementation & Commissioning (Month 4-5)
- Oversees robot installation
- Tests integrated system
- Troubleshoots any issues
- Optimizes final parameters
- Trains operators and maintenance staff
- Validates final performance
Result: System produces 520 units/day (exceeds target), ₹3 crore annual savings achieved, payback period: 4 months. Priya’s design is success.
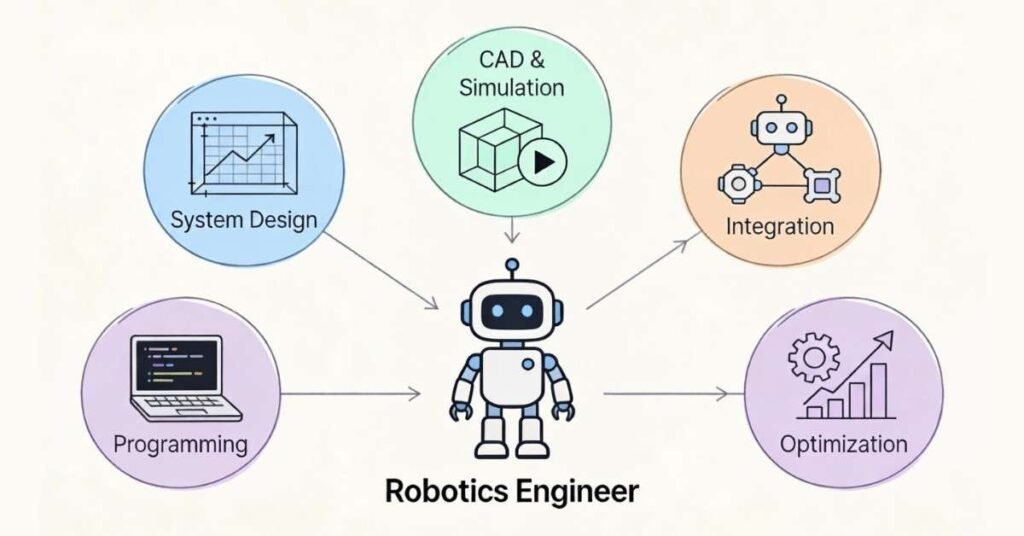
Key Responsibilities of Robotics Engineer
System Design (30%):
- Design robotic automation solutions
- Select appropriate robots for tasks
- Design custom end-effectors and tooling
- Plan system layout and integration
- Create technical specifications
CAD & Simulation (25%):
- Create 3D designs using CAD software
- Simulate robot movements and processes
- Verify designs before hardware procurement
- Design for manufacturability and maintenance
- Optimize designs based on simulations
Implementation & Integration (25%):
- Oversee robot installation
- Integrate with production systems
- Commission and test systems
- Troubleshoot implementation issues
- Optimize system performance
Programming & Optimization (15%):
- Program robot movements and logic
- Optimize cycle times
- Improve accuracy and reliability
- Adapt to new products or process changes
- Document programming
Team Leadership & Training (5%):
- Mentor junior engineers or technicians
- Train operators and maintenance staff
- Lead implementation teams
Communicate with stakeholder
Technical Skills You Must Master
Core Engineering Skills:
- CAD/CAM Software (Critical)
- SolidWorks: Robot system design, 3D modeling
- CATIA: Complex automation systems
- AutoCAD: Layout design, documentation
- Simulation software: Verify designs before building
- Why: Design everything from robot placement to end-effectors
- Learning: 100-150 hours formal training + practice
- ROI: Essential for design work
- Robot Programming (Critical)
- FANUC TPP, ABB RAPID, KUKA KRL language
- Understand kinematics and motion planning
- Path optimization
- Sensor integration
- Why: Program robots to perform tasks safely and efficiently
- Learning: 60-100 hours per robot brand
- ROI: Essential for your role
- Electrical Systems Engineering (Important)
- Power distribution and control
- Motor and drive systems
- Sensor integration
- Safety systems and circuits
- PLC integration
- Why: Robots need electrical systems to operate
- Learning: 40-60 hours
- Mechanical Engineering Fundamentals (Important)
- Mechanics and dynamics
- Material strength and selection
- Mechanical design principles
- Tolerances and precision
- Why: Design mechanical components that work reliably
- Learning: Part of engineering degree
- System Integration (Important)
- Integrate robots with conveyors, quality systems
- Design data communication between systems
- Plan workflow automation
- Ensure seamless operation
- Why: Robots don’t work in isolation; must integrate with factory
- Learning: 30-50 hours + on-job experience
Additional Technical Skills:
- Machine learning basics (emerging: AI optimization of robot movements)
- Vision system design (robots need to “see” to position correctly)
- Safety engineering (ISO 10218 for robotics safety standards)
Project management (oversee robot implementation projects)
Soft Skills for Success
Problem-Solving:
- Design solutions to automation challenges
- Troubleshoot implementation issues
- Optimize performance continuously
- Think creatively about new approaches
Communication:
- Explain complex robotic systems to non-technical managers
- Document designs clearly
- Present recommendations persuasively
- Train operators and maintenance staff
Project Management:
- Oversee robot implementation projects
- Manage timelines and budgets
- Coordinate teams
Track RO
Salary Expectations for Robotics Engineer
Junior Robotics Engineer (Year 0-2):
₹50,000 – ₹75,000/month
Robotics Engineer (Year 2-5):
₹75,000 – ₹1,15,000/month
Senior Robotics Engineer (Year 5-8):
₹1,15,000 – ₹1,60,000/month
Lead/Principal Robotics Engineer (Year 8+):
₹1,60,000 – ₹2,20,000+/month
Robotics Manager / Director:
₹1,80,000 – ₹3,00,000+/month
Why Robotics Salaries Are Premium:
- Specialized expertise: Fewer people design robots; high demand
- Business impact: Automation directly improves productivity; measurable ROI
- Strategic importance: Automation is central to manufacturing future
- Scarcity: Severe shortage of robotics engineers globally
International opportunity: Companies compete globally for talent
How to Enter Robotics Engineering
Path 1: Engineering Degree + Robotics Specialization (Recommended)
- Complete engineering degree: Mechanical, Electronics, or Mechatronics (4 years)
- Pursue robotics specialization: Elective courses, projects focused on robotics
- Develop practical skills: Internship with automation/robotics company
- First role: GET Program or Junior Robotics Engineer (₹50,000-75,000/month)
Path 2: Automation Technician to Engineer
- Work as automation technician (3-5 years)
- Gain deep practical experience
- Pursue engineering diploma or degree (2-3 years, part-time)
- Transition to robotics engineer role (salary increase ₹25,000-40,000/month)
Path 3: Accelerated Program
- Post-graduate certification in robotics (6-12 months)
- Requires engineering degree or equivalent
Entry salary: ₹55,000-70,000/month
Certifications That Boost Robotics Engineer Career
Manufacturer-Specific Certifications:
- FANUC Certified Robotics Programmer
- ABB Certified Robotics Engineer
- KUKA Certified Roboticist
- Benefit: ₹10,000-20,000/month salary bump
- Cost: ₹60,000-1,20,000 per certification
- ROI: Very high; manufacturer certifications highly valued
Advanced Certifications:
- Advanced Robotics & AI (if you pursue machine learning in robotics)
- Safety Systems Design (ISO 10218 specialist)
Vision Systems Integratio
The Bottom Line: Robotics Engineer is Tomorrow's Job
Robotics engineers earn top-tier manufacturing salaries because they design the automation that transforms factories. Entry salary ₹50,000-75,000 → 8-year salary ₹1,60,000+. Work is intellectually engaging, strategically important, and future-proof.
If you’re engineering graduate who loves automation and technology, robotics engineering is your career path.
